| Ten Calculations with tensors and characters M. Ephraim, T. Janssen, A. Janner and A. Thiers |
Next: Character tables Up: Examples Previous: Examples
- Invariant magnetic field
- Metric tensor
- Metric tensor in three dimensions
- Elastic tensor
- Vector product
- Magnetoelectric tensor
Invariant tensors
Invariant magnetic field
A magnetic field transforms as a pseudotensor of rank one. For the point group m one has:
| Dimension | 3 |
| Rank | 1 |
| Point group | m (unique axis y) |
| Permutation symmetry | 0 |
| Basis transformation | Identity |
| Type | Pseudotensor |
The result: One free parameter, T![]() , T
, T![]() =T
=T![]() =0.
=0.
Metric tensor
A metric tensor is a symmetric tensor of rank two. In two dimensions one has for the point group 3:
| Dimension | 2 |
| Rank | 2 |
| Point group | 3 |
| Permutation symmetry | (0 1) |
| Basis transformation | Identity |
| Type | Tensor |
The group is generated by a threefold rotation which is represented on a lattice basis
by the matrix
The invariant tensor is:
This stands for the expression
Metric tensor in three dimensions
The metric tensor invariant under the tetragonal group 4 follows from:
| Dimension | 3 |
| Rank | 2 |
| Point group | 4 |
| Permutation symmetry | (0 1) |
| Basis transformation | Identity |
| Type | Tensor |
There are two free parameters:
Elastic tensor
The elastic tensor is a rank-four tensor symmetric in the first two, the second two and exchange of first and second pair of indices.
| Dimension | 3 |
| Rank | 4 |
| Point group | 4 |
| Permutation symmetry | ((0 1)(2 3)) |
| Basis transformation | Identity |
| Type | Tensor |
Result:
There are seven free parameters. For the standard notation where 1=![]() , 2=
, 2=![]() , 3=
, 3=![]() ,
4=
,
4=![]() , 5=
, 5=![]() , 6=
, 6=![]() the elastic tensor becomes the 6
the elastic tensor becomes the 6![]() 6 matrix
6 matrix
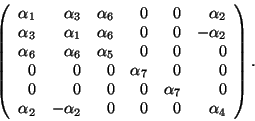
Vector product
A vector product in three dimensions is an antisymmetric rank-two tensor. For the point group 4 one has:
| Dimension | 3 |
| Rank | 2 |
| Point group | 4 |
| Permutation symmetry | [0 1] |
| Basis transformation | Identity |
| Type | Pseudotensor |
There is one free parameter:
![]()
Magnetoelectric tensor
An electric field
| Dimension | 3 |
| Rank | 2 |
| Point group | mm2 (unique axis z) |
| Permutation symmetry | 0 1 |
| Basis transformation | Identity |
| Type | Pseudotensor |
There are two free parameters, and the elements of the invariant tensor are
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]()
Next: Character tables Up: Examples Previous: Examples
